 |
|
Latest News: EPA Finally Begins to Release Dioxin Report
Communities and our Food Supply Poisoned by EPA's 27 Years of Delays in Releasing Dioxin Report
Recent stories on dioxin in the news: |
What is dioxin?
Dioxins and furans are some of the most toxic chemicals known to science. A draft report released for public comment in September 1994 by the US Environmental Protection Agency clearly describes dioxin as a serious public health threat. The public health impact of dioxin may rival the impact that DDT had on public health in the 1960's. According to the EPA report, not only does there appear to be no "safe" level of exposure to dioxin, but levels of dioxin and dioxin-like chemicals have been found in the general US population that are "at or near levels associated with adverse health effects."
Dioxin is a general term that describes a group of hundreds of chemicals that are highly persistent in the environment. The most toxic compound is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin or TCDD. The toxicity of other dioxins and chemicals like PCBs that act like dioxin are measured in relation to TCDD. Dioxin is formed as an unintentional by-product of many industrial processes involving chlorine such as waste incineration, chemical and pesticide manufacturing and pulp and paper bleaching. Dioxin was the primary toxic component of Agent Orange, was found at Love Canal in Niagara Falls, NY and was the basis for evacuations at Times Beach, MO and Seveso, Italy.
Dioxin is formed by burning chlorine-based chemical compounds with hydrocarbons. The major source of dioxin in the environment comes from waste-burning incinerators of various sorts and also from backyard burn-barrels. Dioxin pollution is also affiliated with paper mills which use chlorine bleaching in their process and with the production of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plastics and with the production of certain chlorinated chemicals (like many pesticides).
Yes. The EPA report confirmed that dioxin is a cancer hazard to people. In 1997, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) -- part of the World Health Organization -- published their research into dioxins and furans and announced on February 14, 1997, that the most potent dioxin, 2,3,7,8-TCDD, is a now considered a Group 1 carcinogen, meaning that it's a known human carcinogen.
Also, in January 2001, the U.S. National Toxicology Program upgraded 2,3,7,8-TCDD from "Reasonably Anticipated to be a Human Carcinogen" to "Known to be a Human Carcinogen." See their reports on dioxins and furans from their 11th Report on Carcinogens (find related documents under 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and Furan). Finally, a 2003 re-analysis of the cancer risk from dioxin reaffirmed that there is no known "safe dose" or "threshold" below which dioxin will not cause cancer.
A July 2002 study shows dioxin to be related to increased incidence of breast cancer.
In addition to cancer, exposure to dioxin can also cause severe reproductive and developmental problems (at levels 100 times lower than those associated with its cancer causing effects). Dioxin is well-known for its ability to damage the immune system and interfere with hormonal systems.
Dioxin exposure has been linked to birth defects, inability to maintain pregnancy, decreased fertility, reduced sperm counts, endometriosis, diabetes, learning disabilities, immune system suppression, lung problems, skin disorders, lowered testosterone levels and much more. For an detailed list of health problems related to dioxin, read the People's Report on Dioxin.
In EPA's dioxin report, they refer to dioxin as hydrophobic (water-fearing) and lipophilic (fat-loving). This means that dioxin, when it settles on water bodies, will rapidly accumulate in fish rather than remain in the water. The same goes for other wildlife. Dioxin works its way to the top of the food chain.
Men have no ways to get rid of dioxin other than letting it break down according to its chemical half-lives. Women, on the other hand, have two ways which it can exit their bodies:
[A TEQ is a dioxin Toxic EQuivalent, calculated by looking at all toxic dioxins and furans and measuring them in terms of the most toxic form of dioxin, 2,3,7,8-TCDD. This means that some dioxins/furans might only count as half a TEQ if it's half as toxic as 2,3,7,8-TCDD.]
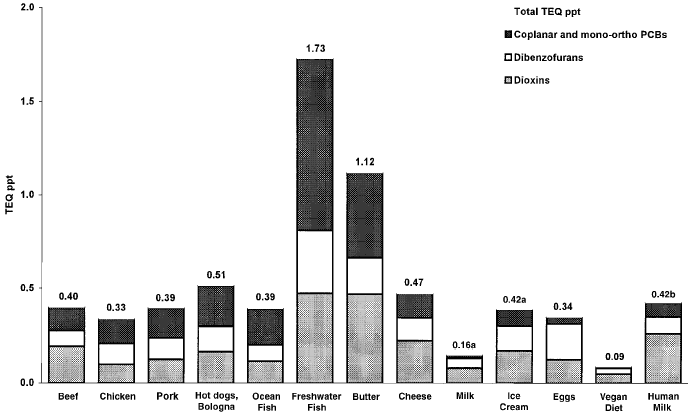
[Chart from May 2001 study by Arnold Schecter et. al., Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A, 63:1–18]
Note: freshwater fish were farm-raised on a diet of meat, which is why they show the highest dioxin levels in this study.
Where Dioxin Comes From:
Read about the convoluted nearly 25+ year history of EPA's dioxin reassessment to learn why it is still not out in final form. For more details on this, read the Behind Closed Doors report about the chemical industry's efforts to block final release of EPA's dioxin report.
U.S. General Accounting Office (GAO) Reports:
Does dioxin cause cancer?
What other health problems are linked to dioxin exposure?
How are we exposed to dioxin?
The major sources of dioxin are in our diet. Since dioxin is fat-soluble, it bioaccumulates, climbing up the food chain. A North American eating a typical North American diet will receive 93% of their dioxin exposure from meat and dairy products (23% is from milk and dairy alone; the other large sources of exposure are beef, fish, pork, poultry and eggs). In fish, these toxins bioaccumulate up the food chain so that dioxin levels in fish are 100,000 times that of the surrounding environment. The best way to avoid dioxin exposure is to reduce or eliminate your consumption of meat and dairy products by adopting a vegan diet. According to a May 2001 study of dioxin in foods, "The category with the lowest [dioxin] level was a simulated vegan diet, with 0.09 ppt.... Blood dioxin levels in pure vegans have also been found to be very low in comparison with the general population, indicating a lower contribution of these foods to human dioxin body burden."
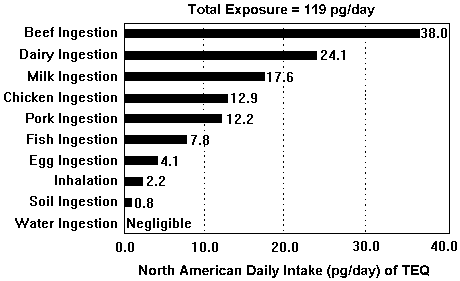
Chart from EPA Dioxin Reassessment Summary 4/94 - Vol. 1, p. 37
(Figure II-5. Background TEQ exposures for North America by pathway)
For more information on dioxin in the food supply...
(May 2001 study in the Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health showing ongoing high levels of dioxins in meat and dairy products)
EPA's Dioxin Reassessment Report and Related Government Documents
Health Effects Reports:
[Read the Alliance for Safe Alternatives' Summary of the Report)]
[Read the Alliance for Safe Alternatives' Summary of the Report]
Links
Good Overviews of Dioxin
Dioxin documents available from the Center for Health, Environment and Justice:
Other Valuable Resources:
Endocrine Disruptors
Dioxins and Incineration:
Anti-Incineration Links:
RACHEL's Environment & Health Weekly IssuesDioxin & Incineration
Dioxin & Health Effects
Dioxin Politics
Dioxin-Related Email Lists / Archives
Ban Toxics List: Ban Toxics List Archives (to subscribe, send a blank email to: ban-toxics-subscribe@yahoogroups.com)There used to be an email list called "dioxin-l" which no longer exists, but its archives are available at the following pages: